Writing your own custom data collection for OMS using SCOM Management Packs
[Unsupported] OMS is a great data collection and analytics tool, but at the moment it also has some limitations. Microsoft has been releasing Integration Pack after Integration Pack and adding features at a decent pace, but unlike the equivalent SCOM Management Packs the IPs are somewhat of a black box. Awhile back, I got frustrated with some of the lack of configuration options in OMS (then Op Insights) and decided to “can opener” some of the features. I figured the best way to do this was to examine some of the management packs that OMS would install into a connected SCOM Management Group and start digging through their contents. Now granted, lately the OMS team has added a lot more customization options than they used to have when I originally traced this out. You can now add custom performance collection rules, custom log collections, and more all from within the OMS portal itself. However, there are still several advantages to being able create your own OMS collection rules in SCOM directly. These include:
Additional levels of configuration customization beyond what’s offered in the OMS portal, such as the ability to target any class you want or use more granular filter criteria than is offered by the portal.
The ability to migrate your collection configuration from one SCOM instance to another. OMS doesn’t currently allow you to export custom configuration.
The ability to do bulk edits through the myriad of tools and editors available for SCOM management packs (it’s much easier to add 50 collection rules to an existing SCOM MP using a simple RegEx find/replace than it is to hand enter them into the OMS SaaS portal).
Digging into the Management Packs automatically loaded into a connected SCOM instance from OMS, we find that there are quite a few. A lot of them still bear the old “System Center Advisor” filenames and display strings from before Advisor got absorbed into OMS, but the IPs also add in a bunch of new MPs that include “IntelligencePacks” in the IDs making them easier to filter by. Many of the type definitions are stored in a pack named (unsurprisingly) Microsoft.IntelligencePacks.Types.
Here is the Event Collection Write Action Module Type Definition:

Now let’s take a look at one of the custom event collection rules I created in the OMS portal to grab all Application log events. These rules are contained in the Microsoft.IntelligencePack.LogManagement.Collection MP:

We can see that the event collection rule for OMS looks an awful lot like a normal event collection rule in SCOM. The ID is automatically generated according to a naming convention that OMS keeps track of which is Microsoft.IntelligencePack.LogManagement.Collection.EventLog. followed by a unique ID string to identify to OMS each specific rule. The only real difference between this rule and a standard event collection rule is the write action, which is the custom write action we saw defined in the Types pack that’s designed to write the event to OMS instead of to the SCOM Data Warehouse. So all you need to do to create your own custom event data collection rule in SCOM is add a reference to the Type MP to your custom MP like:
<Reference Alias="IPTypes"> <ID>Microsoft.IntelligencePacks.Types</ID> <Version>7.0.9014.0</Version> <PublicKeyToken>31bf3856ad364e35</PublicKeyToken> </Reference>
…and then either replace the write action in a standard event collection rule with the following, or add it as an additional write action (you can actually collect to both databases using a single rule):
<WriteAction ID="HttpWA" TypeID="IPTypes!Microsoft.SystemCenter.CollectCloudGenericEvent" />
Now granted, OMS lets you create your own custom event log collection rules using the OMS portal, but at the moment the level of customization and filtering available in the OMS portal is pretty limited. You can specify the name of the log and you can select any combination of three event levels (ERROR, WARNING, and INFOMRATION). You can modify the collection rules to filter them down based on any additional criteria you can create using a standard SCOM management pack. In large enterprises, this can help keep your OMS consumption costs down by leaving out events that you know you do not need to collect.
If we look at Performance Data next, we see that there are two custom Write Action types that are of interest to us:

…and…

…which are the Write Action Modules used for collecting custom performance data and the aggregates for that performance data, respectively. If we take a look at some of the performance collection rules that use these types, we can see how we can use them ourselves. Surprisingly, in the current iteration of OMS they get stored in the Microsoft.IntelligencePack.LogManagement.Collection MP along with the event log collection rules. Here’s an example of the normal collection rule generated in SCOM by adding a rule in OMS:

And just like what we saw with the Event Collection rules, the only difference between this rule and a normal SCOM Performance Collection rule is that instead of the write action to write the data to the Operations Manager DB or DW, we have a “write to cloud” Write Action. So all we need to do in order to add OMS performance collection to existing performance rules is add a reference to the Types MP:
<Reference Alias="IPTypes"> <ID>Microsoft.IntelligencePacks.Types</ID> <Version>7.0.9014.0</Version> <PublicKeyToken>31bf3856ad364e35</PublicKeyToken> </Reference>
And then add the custom write action to the Write Actions section of any of our existing collection rules. Like with the Event Collection rules, we can use multiple write actions so a single rule is capable of writing to Operations Manager database, the data warehouse, and OMS.
<WriteAction ID="WriteToCloud" TypeID="IPTypes!Microsoft.SystemCenter.CollectCloudPerformanceData_PerfIP" />
Now in addition to the standard collection rule we also have an aggregate collection rule that looks like this:

This rule looks almost exactly like the previous collection rule, except for two big differences. One, is that it uses a different write action:
<ConditionDetection ID="Aggregator" TypeID="IPPerfCollection!Microsoft.IntelligencePacks.Performance.PerformanceAggregator">
…and there is an additional Condition Detection that wasn’t present in the standard collection rule for the aggregation:
<ConditionDetection ID="Aggregator" TypeID="IPPerfCollection!Microsoft.IntelligencePacks.Performance.PerformanceAggregator"> <AggregationIntervalInMinutes>30</AggregationIntervalInMinutes> <SamplingIntervalSeconds>10</SamplingIntervalSeconds> </ConditionDetection>
Changing the value for AggregationIntervalInMinutes allows you to change the aggregation interval, which is something that you cannot do in the OMS portal. Otherwise, the native Custom Performance Collection feature of OMS is pretty flexible and allows you to use any Object/Counter/Instance combination you want. However, if your organization already uses SCOM there’s a good chance that you already have a set of custom SCOM MPs that you use for performance data collection. Adding a single write action to these existing rules and creating an additional optional aggregation rule for 100 pre-existing rules is likely easier for an experienced SCOM author than hand-entering 100 custom performance collection rules into the OMS portal. The other benefits from doing it this way include the ability to bulk edit (changing the threshold for all the counters, for example, would be a simple find/replace instead manually changing each rule) and the ability to export this configuration. OMS lets you export data, but not configuration. Any time you spend hand-entering data into the OMS portal would have to be repeated for any other OMS workspace you want to use that configuration in. A custom SCOM MP, however, can be put into source control and re-used in as many different environments as you like.
Note: When making modifications to any rules, do not make changes to the unsealed OMS managed MPs in SCOM. While these changes probably won’t break anything, OMS is the source of record for the content of those MPs. If you make a change in SCOM, it will be disconnected from the OMS config and will likely be overwritten the next time you make a change in OMS.
One last thing. Observant readers may have noticed that every rule I posted is disabled by default. OMS does this for every custom rule, and then enables the rules through the use of an override that’s contained within the same unsealed management pack so this is normal. This is presumably because adjusting an override to enable/disable something is generally considered a “lighter” touch than editing a rule directly, although I don’t see any options to disable any of the collection rules (only delete them).
Azure Resource Tagging Best Practices
We frequently are asked out in the field to help customers understand how tags should be used. Many organizations are worried that tags, being inherently unstructured, will cause confusion. As a result, we’ve come up with a structured way of thinking of and applying tags across your subscription. You can use Azure Resource Manager Policy to enforce this tagging philosophy.
What is a tag?
Tags provide a way to logically organize resources with properties that you define. Tags can be applied to resource groups or resources directly. Tags can then be used to select resources or resource groups from the console, web portal, PowerShell, or the API. Tags are also particularly useful when you need to organize resource for billing or management.
Key Info
- You can only apply tags to resources that support Resource Manager operations
- VMs, Virtual Networks and Storage created through the classic deployment model must be re-deployed through Resource Manager to support tagging
- A good way around this is to tage the resource group they belong too instead.
- All ARM resources support tagging
- VMs, Virtual Networks and Storage created through the classic deployment model must be re-deployed through Resource Manager to support tagging
- Each resource or resource group can have a maximum of 15 tags.
- Tags are key/value pairs, name is limited to 512 characters, value is limited to 256 characters
- Tags are free-form text so consistent correct spelling is very important
- Tags defined on Resource Groups exist only on the group object and do not flow down to the resources under them
- Through the relationship you can easily find resource by filtering by tagged resource group
- We recommend keeping the tags to the resource group unless they are resource specific.
- Each tag is automatically added to the subscription-wide taxonomy
- Application or resource specific tags will "pollute" the tag list for the entire subscription.
Best Practices
We think its important for a customer to leverage at least some of the tags in a structured way. Given the limit on number of tags we recommend tagging at the group level. We don't feel there is currently a need to set them on the resources as you can easily trace down from the Resource Group.
Primarily we recommend a Service/Application/Environment hierarchy along with an environment type, and a billing identifier be reflected in the tags. To do this we recommend spending the time to define an Application hierarchy that spans everything in your subscription. This hierarchy is a key component to both management and billing and allows you to organize the resource groups logically. Its also important that this hierarchy contain additional metadata about the application, like its importance to the organization and the contact in case there is some issue. By storing this outside the tag, say in a traditional CMDB structure, you cut down on the number of tags you need to use and the complexity of tag enforcement, and reduce the risk of tag drift.
Once a taxonomy is agreed on, create the tags for Service/Application and Environment and set them on each Resource Group. Then set a tag for Environment Type to Dev, Test, Production to allow you to target all Dev, all test, or all production later in policy and thru automation.
For the billing identifier, we recommend some type of internal charge code or order number that corresponds to a General Ledger (GL) line item to bill that resource group's usage to. Just these few tags would enable you to determine billing usage for VMs running in production for the finance department.
There are several ways to retrieve billing information and the corresponding tags. More information can be found here: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/documentation/articles/resource-group-using-tags/#tags-and-billing
Recommended Tags
To be prescriptive, we recommend these tags be set on each resource group:
|
Tag Name
|
State
|
Description
|
Tag Value
|
Example
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AppTaxonomy | Required | Provides information on who owns the resource group and what purpose it serves within their application | Org\App\Environment |
USOPS\Finance\Payroll\PayrollTestEnv1
|
| MaintenanceWindow | Optional | Provides a window during which patch and other impacting maintenance can be performed | Window in UTC "day:hour:minute-day:hour:minute" | Tue:04:00-Tue:04:30 |
| EnvironmentType | Required | Provides information on what the resource group is used for (useful for maintenance, policy enforcement, chargeback, etc.) | Dev, Test, UAT, Prod | Test |
| BillingIdentifier | Required | Provides a charge code or cost center to attribute the bill for the resources too | Costcenter | 34821 |
| ExpirationDate | Optional | Provides a date when the environment is expected to be removed by so that reporting can be done to confirm if an environment is still needed | Expiration Date in UTC | 2016-06-15T00:0 |
Over time we’ll have additional posts, scripts and other items that will build on this tagging structure.
New! You may find this post with a PowerShell script useful for reporting on resource group tags
Exposing Azure Stack TP1 to the Public Internet
My previous two posts have been relatively trivial modifications to modify the constraints and parameters exposed in Azure Stack Poc TP1 installer. There was a contrived underlying narrative leading us to here. As TP1 made it in to the wild, my team was tasked with being able to rapidly stand up PoC environments. We eventually landed on an LTI (Lite Touch Installation) type deployment solution which allows us to deploy and re-deploy fresh PoC environments within a couple of hours. This requirement, as expected evolved to exposing the public surfaces of Azure Stack (ARM, The Portal, Storage Accounts, etc.). I’ll attempt to outline the steps required in as concise a manner as possible (hat-tip to AzureStack.eu). The way Azure Stack is currently glued together has the expectation that the Active Directory DNS Name of your deployment will match the DNS suffix used for the publicly accessible surfaces (e.g. portal.azurestack.local). The primary reasons for this is certificates and DNS resolution by the service fabric and clients alike. I’ll expound on this a little later. It was relatively simple to automate the exposing a new environment by allowing configuration to follow consistent convention. As a practical example, We have a number of blade chassis within our datacenters. In each chassis where we host PoC environments, each blade is on a different subnet with a specific set of IP addresses that will be exposed to the internet (if needed) via 1-to-1 NAT.
Each blade is on a different vlan and subnet for a reason. Azure Stack's use of VXLAN to talk between hosts in a scale out configuration means that if you try to stand up two hosts on the same layer 2 segment, you will have IP address conflicts between them on the private azure stack range. There are ways in the config to change the VXLAN IDs and avoid this, but it's simpler to just use separate VLANs. Each blade is on a dedicated private space VLAN, and is then NAT'd to the public internet thru a common router/firewall with 1:1 NATs on the appropriate addresses. This avoids having to put the blade directly on the internet, and a Static NAT avoids any sort of port address translation.
Prerequisites
You will need at least 5 public IP addresses and access to manage the DNS zone for the domain name you will be using. Our domain used for the subsequent content will be yourdomain.com (replace with your domain name) and I will assume that the ‘Datacenter’ (Considered the public network for Stack) network for your Azure Stack installation is will apply 1-to-1 NAT on the appropriate IP addresses exposed to the public internet.
We’ll use a hypothetical Internal IP address set of 172.20.10.33-172.20.10.39 and External IP address set of 38.x.x.30-38.x.x.34 for this example. The process I will describe will require static IP addressing on the NAT public interface. These options are required parameters of the installation along with the desired custom Active Directory DNS Domain Name.
Networking
Azure Stack Virtual IP Addresses
| Role | Internal VIP | ‘Datacenter’ Network IP | External IP |
| Portal and API | 192.168.133.74 | 172.20.10.33 | 38.x.x.30 |
| Gallery | 192.168.133.75 | 172.20.10.34 | 38.x.x.31 |
| CRP, NRP, SRP | 192.168.133.31 | 172.20.10.35 | 38.x.x.32 |
| Storage Account | 192.168.133.72 | 172.20.10.36 | 38.x.x.33 |
| Extensions | 192.168.133.71 | 172.20.10.37 | 38.x.x.34 |
Azure Stack VM IP Addresses
| Role | Internal IP | ‘Datacenter’ Network IP |
| ADVM | 192.168.100.2 | 172.20.10.38 |
| ClientVM | 192.168.200.101 | 172.20.10.39 |
DNS
We will need to start a new deployment with our desired domain name. Please see my previous post Changing Azure Stack’s Active Directory DNS Domain to something other than AzureStack.local on how to make this an installation parameter. Please note, modifications to the additional resource provider (e.g. Sql and Web Apps) installers will also be required. We just changed instances of azurestack.local to $env:USERDNSDOMAIN as they are primarily executed within the Azure Stack Active Directory context.
To be honest, I probably should have addressed this in the previous post. If the Active Directory DNS domain name you wish to use will be resolvable by the host while deploying the stack I recommend you simply add an entry to the HOSTS file prior to initiating installation. We ended up adding this to our deployment process as we wanted to leave public DNS entries in place for certain environments. In this version we know the resultant IP address of the domain controller that will be created.
Add an entry like such:
192.168.100.2 yourdomain.com
You will need to add a number of A records within your public DNS zone.
| A Record | IP Address |
| api.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.30 |
| portal.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.30 |
| gallery.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.31 |
| srp.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.32 |
| nrp.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.32 |
| srp.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.32 |
| xrp.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.32 |
| *.compute.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.32 |
| *.storage.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.32 |
| *.network.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.32 |
| *.blob.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.33 |
| *.queue.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.33 |
| *.table.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.33 |
| *.adminextensions.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.34 |
| *.tenantextensions.yourdomain.com | 38.x.x.34 |
Installation
The NAT IP addressing and Active Directory DNS domain name need to be supplied to the PoC installation. A rough script running in the context of the installation folder will look something like this:
[powershell]
$ADDomainName="yourdomain.com" $AADTenant="youraadtenant.com" $AADUserName="yourStackUser@$AADTenant" $AADPassword=ConvertTo-SecureString -String "ThisIsYourAADPassword!" -AsPlainText -Force $AdminPassword=ConvertTo-SecureString -String "ThisIsYourStackPassword!" -AsPlainText -Force $NATVMStaticIP="172.20.10.30/24" $NATVMStaticGateway="172.20.10.1" $AADCredential=New-Object pscredential($AADUserName,$AADPassword) $DeployScript= Join-Path $PSScriptRoot "DeployAzureStack.ps1" &$DeployScript -ADDomainName $ADDomainName -AADTenant $AADTenant ` -AdminPassword $AdminPassword -AADCredential $AADCredential ` -NATVMStaticIP $NATVMStaticIP -NATVMStaticGateway $NATVMStaticGateway -Verbose -Force
[/powershell]
Configuring Azure Stack NAT
The public internet access, both ingress and egress, is all controlled via Routing and Remote Access and networking within the NATVM virtual machine. There are effectively three steps you will need to undertake that will require internal VIP addresses within the stack and the public IP addresses you wish to associate with your deployment. This process can be completed through the UI, however, given the nature of our lab, doing this in a scriptable fashion was an imperative. If you must do this by hand, start by opening the Routing and Remote Access MMC on the NATVM in order to modify the public NAT settings.
Create a Public IP Address Pool within the RRAS NAT configuration.
Create IP Address reservations for the all of the IP addresses for which the public DNS entries were created within the RRAS NAT configuration. Note incoming sessions are required for all the Azure Stack public surfaces.
Associate the additional Public IP addresses with the NATVM Public Interface in the NIC settings. (This is a key step that isn't covered elsewhere)
I told you that we needed to script this and unfortunately, as far as I can tell, the easiest way is still through the network shell netsh.exe. The parameters for our script are the same for every deployment and a script file for netsh is dynamically created. If you already have a large amount of drool on your keyboard from reading this tome, I'll cut to the chase and give you a sample to drive netsh. In the following example Ethernet 2 is the 'Public' Adapter on the NATVM and our public IP Addresses are in the 172.20.10.0/24 network and will be mapped according to the previous table
[text]
#Set the IP Addresses pushd interface ipv4 add address name="Ethernet 2" address=172.20.27.38 mask=255.255.255.0 add address name="Ethernet 2" address=172.20.27.31 mask=255.255.255.0 add address name="Ethernet 2" address=172.20.27.33 mask=255.255.255.0 add address name="Ethernet 2" address=172.20.27.35 mask=255.255.255.0 add address name="Ethernet 2" address=172.20.27.34 mask=255.255.255.0 add address name="Ethernet 2" address=172.20.27.37 mask=255.255.255.0 add address name="Ethernet 2" address=172.20.27.36 mask=255.255.255.0 add address name="Ethernet 2" address=172.20.27.32 mask=255.255.255.0 add address name="Ethernet 2" address=172.20.27.39 mask=255.255.255.0 popd #Configure NAT pushd routing ip nat #NAT Address Pool add addressrange name="Ethernet 2" start=172.20.27.31 end=172.20.27.39 mask=255.255.255.0 #NAT Pool Reservations add addressmapping name="Ethernet 2" public=172.20.27.38 private=192.168.100.2 inboundsessions=disable add addressmapping name="Ethernet 2" public=172.20.27.31 private=192.168.5.5 inboundsessions=disable add addressmapping name="Ethernet 2" public=172.20.27.33 private=192.168.133.74 inboundsessions=enable add addressmapping name="Ethernet 2" public=172.20.27.35 private=192.168.133.31 inboundsessions=enable add addressmapping name="Ethernet 2" public=172.20.27.34 private=192.168.133.75 inboundsessions=enable add addressmapping name="Ethernet 2" public=172.20.27.37 private=192.168.133.71 inboundsessions=enable add addressmapping name="Ethernet 2" public=172.20.27.36 private=192.168.133.72 inboundsessions=enable add addressmapping name="Ethernet 2" public=172.20.27.32 private=192.168.200.101 inboundsessions=disable add addressmapping name="Ethernet 2" public=172.20.27.39 private=192.168.100.12 inboundsessions=disable popd
[/text]
If I haven’t lost you already and you would like to achieve this with PowerShell, the following script uses PowerShell direct to configure NAT in the previously demonstrated manner taking a PSCredential (an Adminstrator on NATVM) and an array of very simple objects representing the (for now) constant NAT mappings.
They can easily be stored in JSON (and I insist that is pronounced like the given name Jason) for easy serialization/de-serialization
[powershell] #requires -Modules NetAdapter,NetTCPIP -Version 5.0 [CmdletBinding()] param ( [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [Object[]] $Mappings, [Parameter(Mandatory=$false)] [Int32] $PoolSize=8, [Parameter(Mandatory=$false)] [String] $NatVmInternalIP="192.168.200.1", [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [pscredential] $Credential, [Parameter(Mandatory=$false)] [String] $NatVmName="NATVM" )
$ActivityId=33
$NatSetupScriptBlock= { [CmdletBinding()] param()
$VerbosePreference=$Using:VerbosePreference $ParentId=$Using:ActivityId $NatVmInternalIP=$Using:NatVmInternalIP $Mappings=@($Using:Mappings) $AddressPoolSize=$Using:PoolSize
#region Helper Methods
<# .SYNOPSIS Converts a CIDR or Prefix Length as string to a Subnet Mask .PARAMETER CIDR The CIDR or Prefix Length to convert #> Function ConvertTo-SubnetMaskFromCIDR { [CmdletBinding()] [OutputType([String])] param ( [Parameter(Mandatory=$true,ValueFromPipeline=$true)] [String] $CIDR ) $NetMask="0.0.0.0" $CIDRLength=[System.Convert]::ToInt32(($CIDR.Split('/')|Select-Object -Last 1).Trim()) Write-Debug "Converting Prefix Length $CIDRLength from input $CIDR" switch ($CIDRLength) { {$_ -gt 0 -and $_ -lt 8} { $binary="$( "1" * $CIDRLength)".PadRight(8,"0") $o1 = [System.Convert]::ToInt32($binary.Trim(),2) $NetMask = "$o1.0.0.0" break } 8 {$NetMask="255.0.0.0"} {$_ -gt 8 -and $_ -lt 16} { $binary="$( "1" * ($CIDRLength - 8))".PadRight(8,"0") $o2 = [System.Convert]::ToInt32($binary.Trim(),2) $NetMask = "255.$o2.0.0" break } 16 {$NetMask="255.255.0.0"} {$_ -gt 16 -and $_ -lt 24} { $binary="$("1" * ($CIDRLength - 16))".PadRight(8,"0") $o3 = [System.Convert]::ToInt32($binary.Trim(),2) $NetMask = "255.255.$o3.0" break } 24 {$NetMask="255.255.255.0"} {$_ -gt 24 -and $_ -lt 32} { $binary="$("1" * ($CIDRLength - 24))".PadRight(8,"0") $o4 = [convert]::ToInt32($binary.Trim(),2) $NetMask= "255.255.255.$o4" break } 32 {$NetMask="255.255.255.255"} } return $NetMask }
Function Get-ExternalNetAdapterInfo { [CmdletBinding()] param ( [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [String] $ExcludeIP )
$AdapterInfos=@() $NetAdapters=Get-NetAdapter -Physical foreach ($NetAdapter in $NetAdapters) { if($NetAdapter.Status -eq 'Up') { $AdapIpAddress=$NetAdapter|Get-NetIPAddress -AddressFamily IPv4 $AdapterInfo=New-Object PSObject -Property @{ Adapter=$NetAdapter; IpAddress=$AdapIpAddress; } $AdapterInfos+=$AdapterInfo } }
$DesiredAdapter=$AdapterInfos|Where-Object{$_.IPAddress.IPAddress -ne $ExcludeIP} return $DesiredAdapter }
Function Get-NetshScriptContent { [CmdletBinding()] param ( [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [Object] $ExternalAdapter, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [Object[]] $NatMappings, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [Int32] $PoolSize )
#Retrieve the Network Adapters $ExternalAddress=$ExternalAdapter.IPAddress.IPAddress $ExternalPrefixLength=$ExternalAdapter.IPAddress.PrefixLength $ExternalAdapterName=$ExternalAdapter.Adapter.Name Write-Verbose "External Network Adapter [$ExternalAdapterName] $($ExternalAdapter.Adapter.InterfaceDescription) - $ExternalAddress" $IpPieces=$ExternalAddress.Split(".") $LastOctet=[System.Convert]::ToInt32(($IpPieces|Select-Object -Last 1)) $IpFormat="$([String]::Join(".",$IpPieces[0..2])).{0}" $PublicCIDR="$IpFormat/{1}" -f 0,$ExternalPrefixLength
$AddressPoolStart=$IpFormat -f ($LastOctet + 1) $AddressPoolEnd=$IpFormat -f ($LastOctet + 1 + $PoolSize) $ExternalNetMask=ConvertTo-SubnetMaskFromCIDR -CIDR $PublicCIDR Write-Verbose "Public IP Address Pool Start:$AddressPoolStart End:$AddressPoolEnd Mask:$ExternalNetMask"
$TargetIpEntries=@() $ReservationEntries=@() foreach ($Mapping in $NatMappings) { Write-Verbose "Evaluating Mapping $($Mapping.name)" $TargetPublicIp=$IpFormat -f $Mapping.publicIP $TargetIpEntry="add address name=`"{0}`" address={1} mask={2}" -f $ExternalAdapterName,$TargetPublicIp,$ExternalNetMask $TargetIpEntries+=$TargetIpEntry if($Mapping.allowInbound) { $InboundEnabled="enable" } else { $InboundEnabled="disable" } $ReservationEntry="add addressmapping name=`"{0}`" public={1} private={2} inboundsessions={3}" -f $ExternalAdapterName,$TargetPublicIp,$Mapping.internalIP,$InboundEnabled $ReservationEntries+=$ReservationEntry }
$NetshScriptLines=@() #IP Addresses $NetshScriptLines+="#Set the IP Addresses" $NetshScriptLines+="pushd interface ipv4" $TargetIpEntries|ForEach-Object{$NetshScriptLines+=$_} $NetshScriptLines+="popd" #NAT $NetshScriptLines+="#Configure NAT" $NetshScriptLines+="pushd routing ip nat" $NetshScriptLines+="#NAT Address Pool" $NetshScriptLines+="add addressrange name=`"{0}`" start={1} end={2} mask={3}" -f $ExternalAdapterName,$AddressPoolStart,$AddressPoolEnd,$ExternalNetMask $NetshScriptLines+="#NAT Pool Reservations" $ReservationEntries|ForEach-Object{$NetshScriptLines+=$_} $NetshScriptLines+="popd"
return $NetshScriptLines }
#endregion
#region Execution
Write-Progress -ParentId $ParentId -Activity "Publishing Azure Stack" -Status "Detecting Public Adapter" -PercentComplete 5 $ExternalNetAdapter=Get-ExternalNetAdapterInfo -ExcludeIP $NatVmInternalIP Write-Progress -Activity "Publishing Azure Stack" ` -Status "External Network Adapter [$($ExternalNetAdapter.Adapter.Name)] $($ExternalNetAdapter.Adapter.InterfaceDescription) - $($ExternalNetAdapter.IPAddress.IPAddress)" -PercentComplete 10 if($ExternalNetAdapter -eq $null) { throw "Unable to resolve the public network adapter!" } Write-Progress -ParentId $ParentId -Activity "Publishing Azure Stack" -Status "Creating Network Script" -PercentComplete 25 $NetshScript=Get-NetshScriptContent -ExternalAdapter $ExternalNetAdapter -NatMappings $Mappings -PoolSize $AddressPoolSize #Save the file.. $NetShScriptPath=Join-Path $env:TEMP "configure-nat.txt" $NetShScriptExe= Join-Path $env:SystemRoot 'System32\netsh.exe'
#Run NetSh Set-Content -Path $NetShScriptPath -Value $NetshScript -Force Write-Progress -ParentId $ParentId -Activity "Publishing Azure Stack" -Status "Created Network Script $NetShScriptPath" -PercentComplete 50
Write-Progress -ParentId $ParentId -Activity "Publishing Azure Stack" -Status "Configuring NAT $NetShScriptExe -f $NetShScriptPath" -PercentComplete 70 $NetShProcess=Start-Process -FilePath $NetShScriptExe -ArgumentList "-f $NetShScriptPath" -PassThru -Wait Write-Progress -ParentId $ParentId -Activity "Publishing Azure Stack" -Status "Restarting RRAS.." -PercentComplete 90 Restart-Service -Name RemoteAccess Write-Progress -ParentId $ParentId -Activity "Publishing Azure Stack" -PercentComplete 100 -Completed
#endregion
$ConfigureResult=New-Object PSObject -Property @{ NetSHProcess=$NetShProcess; NetSHScript=$NetShScript; } return $ConfigureResult
}
Write-Progress -Id $ActivityId -Activity "Configuring NAT" -Status "Publishing Azure Stack TP1 PoC $NatVmName as $($Credential.UserName)..." -PercentComplete 10 $result=Invoke-Command -ScriptBlock $NatSetupScriptBlock -Credential $Credential -VMName $NatVmName Write-Progress -Id $ActivityId -Activity "Configuring NAT" -PercentComplete 100 -Completed
return $result [/powershell]
Certificates
You will need to export the root certificate from the CA for your installation for importing on any clients that will access your deployment. I will leave the use of publicly trusted certificates outside the scope of this post, nor will I address the use of a CA other than the one deployed with Active Directory. The expanse of aforementioned DNS entries should give you an idea of how many certificates you will need to obtain to avoid this step with any clients. In the case of operating public Azure, this is one place where it must be very nice being a Trusted Root Certificate Authority.
Exporting the root certificate is very simple as the PoC host system is joined to the domain which hosts the Azure Stack CA, both roles reside on the ADVM. To export the Root certificate to your desktop run this simple one-liner in the PowerShell console of your Host system (the same command will work from the ClientVM).
[powershell] Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:\LocalMachine\Root| ` Where-Object{$_.Subject -like "CN=AzureStackCertificationAuthority*"}| ` Export-Certificate -FilePath "$env:USERPROFILE\Desktop\$($env:USERDOMAIN)RootCA.cer" -Type CERT [/powershell]
The process for importing this certificate on your client will vary depending on the OS version; as such I will avoid giving a scripted method.
Right click the previously exported certificate.
Choose Current User for most use-cases.
Select Browse for the appropriate store.
Select Trusted Root Certificate Authorities
Confirm the Import Prompt
Enjoying the Results
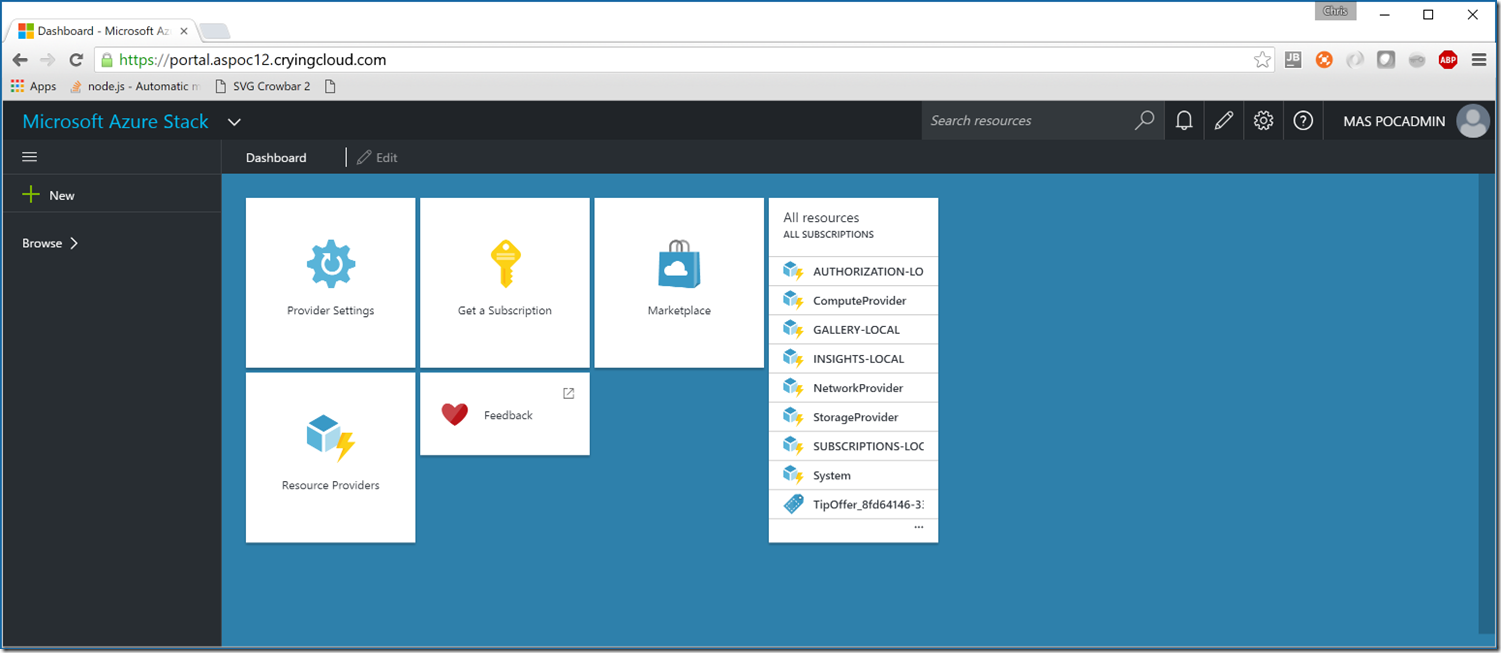
If we now connect to the portal, we should be prompted to login via Azure Active Directory and upon authentication you should be presented with a familiar portal.

You can also connect with the Azure Cmdlets if that is more your style. We'll make a slight modification to the snippet from the post by Mike De Luca How to Connect to Azure Stack via PowerShell.
[powershell] $ADDomainName="yourdomain.com" $AADTenant="youraadtenant.com" $AADUserName="yourStackUser@$AADTenant" $AADPassword=ConvertTo-SecureString -String "ThisIsYourAADPassword!" -AsPlainText -Force $AADCredential=New-Object PSCredential($AADUserName,$AADPassword) $StackEnvironmentName="Azure Stack ($ADDomainName)" $StackEnvironment=Add-AzureRmEnvironment -Name $StackEnvironmentName ` -ActiveDirectoryEndpoint ("https://login.windows.net/$AADTenant/") ` -ActiveDirectoryServiceEndpointResourceId "https://$ADDomainName-api/" ` -ResourceManagerEndpoint ("Https://api.$ADDomainName/") ` -GalleryEndpoint ("Https://gallery.$($ADDomainName):30016/") ` -GraphEndpoint "https://graph.windows.net/" Add-AzureRmAccount -Environment $StackEnvironment -Credential $AADCredential [/powershell]
Your Azure Stack TP1 PoC deployment should now be available to serve all clients from the public internet in an Azure Consistent manner.
[Unsupported]
Changing Azure Stack’s DNS and AD Domain to something other than AzureStack.local
This is another installer modification for Azure Stack TP1 PoC, that unfortunately will require editing more than one file. I find the fact this edit is necessary, puzzling; once again we will start by mounting MicrosoftAzureStackPOC.vhdx. We will start within PocDeployment\Test-AzureStackDeploymentParameters.ps1 at line 68:
[powershell]$ADDomainName = "AzureStack.local"[/powershell]
Why is this not a parameter? We will also ignore the fact we are editing signed scripts and go ahead and make it one, first deleting that line and subsequently modifying the parameter block (leaving the default as azurestack.local).
[powershell] [CmdletBinding()] Param ( [string] [Parameter(Mandatory = $true)] $PackagePath,
[SecureString] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $AdminPassword,
[PSCredential] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $AADCredential,
[string] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $AADTenant,
[PSCredential] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $TIPServiceAdminCredential,
[PSCredential] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $TIPTenantAdminCredential,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] [Nullable[bool]] $UseAADChina,
[String] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $NATVMStaticIP,
[String] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $NATVMStaticGateway,
[String] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $PublicVLan = $null,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] [string] $ProxyServer,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] [string] $ADDomainName = "AzureStack.local",
[Switch] $Force ) [/powershell]
We will also update yet another hard coded value this time in PocDeployment\Invoke-DeploymentLogCollection.ps1. Look to line 106 and you will find a line like this:
[powershell] ('PublicIPAddresses','GatewayPools','GateWays','loadBalancers','loadBalancerMuxes','loadBalancerManager/config','networkInterfaces','virtualServers','Servers','credentials','macPools','logicalnetworks','accessControlLists') | % { JSONGet -NetworkControllerRestIP "NCVM.azurestack.local" -path "/$_" -Credential $credential | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 20 > "$destination\NC\$($_ -replace '/','').txt" } [/powershell]
Replace the hard coded azurestack.local value with the existing!!! parameter:
[powershell] ('PublicIPAddresses','GatewayPools','GateWays','loadBalancers','loadBalancerMuxes','loadBalancerManager/config','networkInterfaces','virtualServers','Servers','credentials','macPools','logicalnetworks','accessControlLists') | % { JSONGet -NetworkControllerRestIP "NCVM.$($parameters.ADDomainName)" -path "/$_" -Credential $credential | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 20 > "$destination\NC\$($_ -replace '/','').txt" } [/powershell]
Finally we need to modify the main installer script (in duplicate). DeployAzureStack.ps1 is located both in the root of the Azure Stack TP1 zip file you downloaded and the Installer directory within MicrosoftAzureStackPOC.vhdx. You can modify the file once and copy it to the other location in whatever order you choose. We are going to start by adding a parameter, $ADDomainName, for the Active Directory DNS name (again leaving the default as azurestack.local):
[powershell] [CmdletBinding()] param ( [SecureString] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $AdminPassword,
[PSCredential] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $AADCredential,
[string] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $AADTenant,
[PSCredential] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $TIPServiceAdminCredential,
[PSCredential] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $TIPTenantAdminCredential,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] [Nullable[bool]] $UseAADChina,
[String] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $NATVMStaticIP = $null, #eg: 10.10.10.10/24
[String] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $NATVMStaticGateway = $null, #eg: 10.10.10.1
[String] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $PublicVLan = $null, #eg: 305
[String] [Parameter(Mandatory = $false)] $ProxyServer,
[String] [Parameter(Mandatory=$false)] $ADDomainName="azurestack.local",
[Switch] $Force,
[Switch] $NoAutoReboot ) [/powershell]
Modify line 102 to accomodate the parameter we’ve created in this and Test-AzureStackDeploymentParameters.ps1. The original line will look like this:
[powershell] $Parameters = & "$DeploymentScriptPath\Test-AzureStackDeploymentParameters.ps1" -PackagePath $PSScriptRoot -AdminPassword $AdminPassword -AADCredential $AADCredential -AADTenant $AADTenant -TIPServiceAdminCredential $TIPServiceAdminCredential -TIPTenantAdminCredential $TIPTenantAdminCredential -UseAADChina $UseAADChina -NATVMStaticIP $NATVMStaticIP -NATVMStaticGateway $NATVMStaticGateway -PublicVLan $PublicVLan -ProxyServer $ProxyServer -Force:$Force [/powershell]
Add the ADDomainName parameter:
[powershell] $Parameters = & "$DeploymentScriptPath\Test-AzureStackDeploymentParameters.ps1" -PackagePath $PSScriptRoot -AdminPassword $AdminPassword -AADCredential $AADCredential -AADTenant $AADTenant -TIPServiceAdminCredential $TIPServiceAdminCredential -TIPTenantAdminCredential $TIPTenantAdminCredential -UseAADChina $UseAADChina -NATVMStaticIP $NATVMStaticIP -NATVMStaticGateway $NATVMStaticGateway -ADDomainName $ADDomainName -PublicVLan $PublicVLan -ProxyServer $ProxyServer -Force:$Force [/powershell]
Unmount the VHD and install to a new domain if you so desire.
[Unsupported]
Modifying Azure Stack POC Install Constraints
Azure Stack’s specific hardware requirements, specifically RAM and Storage, may prevent one from being able to install on available kit. This is a pretty well known “hack”, however this is enterprise IT so redundancy is a good thing. The constraints are pretty simple to modify for your particular situation.
Once again, we’ll start by mounting the MicrosoftAzureStackPOC.vhdx (I won’t bother covering how to do that).
All of the hardware constraints are enforced through functions in PocDeployment\Invoke-AzureStackDeploymentPrecheck.ps1.
If you look at line 62 within the function CheckDisks you will find a statement that looks like this:
[powershell]$physicalDisks = Get-PhysicalDisk | Where-Object { $_.CanPool -eq $true -and ($_.BusType -eq 'RAID' -or $_.BusType -eq 'SAS' -or $_.BusType -eq 'SATA') }[/powershell]
You can choose to add another allowed bus type e.g. ISCSI, or if you are really adventurous just remove the entire AND clause.
[powershell]$physicalDisks = Get-PhysicalDisk | Where-Object { $_.CanPool -eq $true -and ($_.BusType -eq 'RAID' -or $_.BusType -eq 'SAS' -or $_.BusType -eq 'SATA' -or $_.BusType -eq 'ISCSI') }[/powershell]
or
[powershell]$physicalDisks = Get-PhysicalDisk | Where-Object { $_.CanPool -eq $true}[/powershell]
To modify the RAM contraints look further down, and at line 98 with CheckRAM you will find a very simple test:
[powershell]</p> <p>if ($totalMemoryInGB -lt 96) {<br> throw "Check system memory requirement failed. At least 96GB physical memory is required."<br>}</p> <p>[/powershell]
Modify the value as appropriate:
[powershell]</p> <p>if ($totalMemoryInGB -lt 64) {<br> throw "Check system memory requirement failed. At least 64GB physical memory is required."<br>}</p> <p>[/powershell]
Unmount the VHD, and you are done. It is worth reiterating that these constraints exist for a reason, and in adjusting or bypassing you should have appropriate expectations for performance and/or stability.
[Unsupported]
Topic Search
Posts by Date
- August 2025 1
- March 2025 1
- February 2025 1
- October 2024 1
- August 2024 1
- July 2024 1
- October 2023 1
- September 2023 1
- August 2023 3
- July 2023 1
- June 2023 2
- May 2023 1
- February 2023 3
- January 2023 1
- December 2022 1
- November 2022 3
- October 2022 7
- September 2022 2
- August 2022 4
- July 2022 1
- February 2022 2
- January 2022 1
- October 2021 1
- June 2021 2
- February 2021 1
- December 2020 2
- November 2020 2
- October 2020 1
- September 2020 1
- August 2020 1
- June 2020 1
- May 2020 2
- March 2020 1
- January 2020 2
- December 2019 2
- November 2019 1
- October 2019 7
- June 2019 2
- March 2019 2
- February 2019 1
- December 2018 3
- November 2018 1
- October 2018 4
- September 2018 6
- August 2018 1
- June 2018 1
- April 2018 2
- March 2018 1
- February 2018 3
- January 2018 2
- August 2017 5
- June 2017 2
- May 2017 3
- March 2017 4
- February 2017 4
- December 2016 1
- November 2016 3
- October 2016 3
- September 2016 5
- August 2016 11
- July 2016 13